Rheumatoid Arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease marked by a symmetrical arthritis affecting multiple joints.
Symptoms:
• Rheumatoid Arthritis is a disease most commonly seen amongst women in the reproductive age group, the highest incidence being in age group of 25 to 55 years.
• The symptoms typically result from inflammation of joints and tendons.
• The earliest symptom is early morning joint stiffness, lasting more than an hour and easing with physical activity.
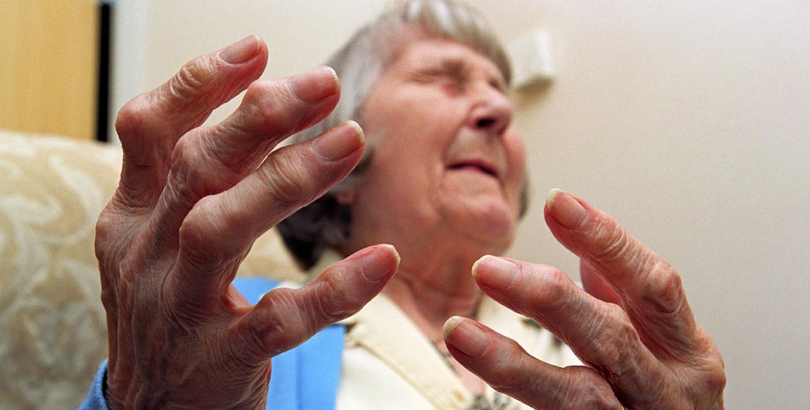
• The earliest joints involved are typically small joints of the hands and the feet. The pattern of involvement initially can be a single joint, oligoarticular (5 joints), usually in a symmetric distribution.
• Progressive destruction of the joints and soft tissues may lead to chronic irreversible deformities.
• The only portion of the spine involved is the cervical spine, with the joint between first and second cervical being the commonest location. This involvement has the potential to cause a major neurological dysfunction.
• Extra-articular manifestations (involving other organ systems) may occur in course of he disease, sometimes even before joint involvement.
• They include nodules under the skin, fibrosis of lungs, pleurisy, rarely cardiac involvement causing cardio-myopathy, vasculitis causing painful skin ulcers, anemia etc.
Cause:
• Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease, which means the immune system of the body produces immunity against its own cells, in this case against joints, tendons and soft tissues around joints.
• The cause of this autoimmunity is a complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors.
Treatment:
• The diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis is a clinical one, aided by help of serum marker antibodies such as RA factor and Anti-CCP antibodies.
• Major aim of the treatment is reducing joint inflammation and preventing joint damage and deformities.
• The medications used in treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis can be broadly divided into nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), glucocorticoids (steroids), conventional disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS) and newer biological agents.
• Based on patient’s clinical status, generally a combination of drugs is used, modified according to disease status evaluated from time to time.
• Surgical procedures may be used to improve pain and disability if there is failure of medical treatment.
• Physical therapy and assisting devices: All patients should receive a prescription for exercise and physical activity. Dynamic strength training and physical activity coaching (emphasizing 30 minutes of moderately intensive activity most days a week) has been shown to improve muscle strength and health status.