Diabetes is a disease, hyperglycemia is a condition.
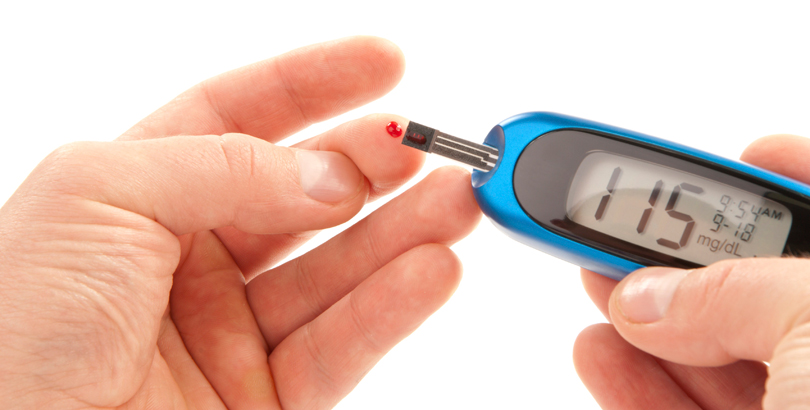
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar (glucose), for diabetes patients can be a serious health hazard. Spike in bloodsugar causes hyperglycemia. There are two types of hyperglycemia:
Fasting hyperglycemia
When blood sugar greater than 130 mg/dL (mg/deciliter) after fasting (for at least 8 hours).
Postprandial or after-meal hyperglycemia
When blood sugar usually greater than 180 mg/dL.
Non diabetic people usually have 140mg/dL, but someimtes after meal there can be an increase in blood sugar level. Consistently elevated high post-meal blood sugar levels can be an indicator that a person has or is at high risk for developing type 2 diabetes.
HbA1c blood test reveals that when a person with diabetes has hyperglycemia frequently, or for long periods of time, damage to nerves, blood vessels, and other body organs can occur. Hyperglycemia can also lead to more serious conditions, including ketoacidosis – mostly in people with type 1 diabetes, and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome (HHNS) in people with type 2 diabetes or in people at risk for type 2 diabetes.
Hyperglycemia can be extremely hazardous, so early diagnosis and treatment is important.
What Causes Hyperglycemia in Diabetes?
- Infection
- Illness
- Increased stress
- Decreased activity or exercising less than usual
- Skipping or forgetting your insulin or oral glucose-lowering medicine
- Eating too many grams of carbohydrates for the amount of insulin administered or just eating too many grams of carbohydrates in general
- Strenuous physical activity, especially when blood glucose levels are high to begin with, and insulin levels are low
What Are the Symptoms of Hyperglycemia in Diabetes?
If you have diabetes, it is important to know the early signs of hyperglycemia. If hyperglycemia is left untreated, it may develop into ketoacidosis (for type 1 diabetes) or HHNS (for type 2 diabetes), both of which are serious emergencies.
Early signs of hyperglycemia in diabetes may include:
- Increased thirst
- Headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue (weak, tired feeling)
- Weight loss
- Blood sugar more than 180 mg/dL
Prolonged hyperglycemia in diabetes may result in:
- Vaginal and skin infections
- Slow-healing cuts and sores
- Decreased vision
- Nerve damage causing painful cold or insensitive feet, loss of hair on the lower extremities, and/or erectile dysfunction
- Stomach and intestinal problems such as chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Damage to your eyes, blood vessels, or kidneys